In today’s era of networking, IT professionals are faced with a transformed landscape. Gone are the days when all of an organization’s devices are interconnected on a single network with a shared address space. Due to the evolved needs of today’s organizations where office premises can span multiple floors with individuals in the same department working on separate floors but needing access to the same specific resources, a segmentation of networks is needed. This segmentation should allow organizations to still share common resources while allowing department specific resources to be accessible to only individuals who belong to that department. This is where virtual local area networks (VLAN) come in.
VLANs are a logical grouping of devices on a physical local area network (LAN). They allow network administrators to segment a single LAN into multiple networks, each with its own broadcast domain. Let’s say for example you work for a hospital and want to ensure that you isolate the various departments such as the patient care department, the admin department, and the research department, you can use VLANs to get it done in an easy and seamless manner.
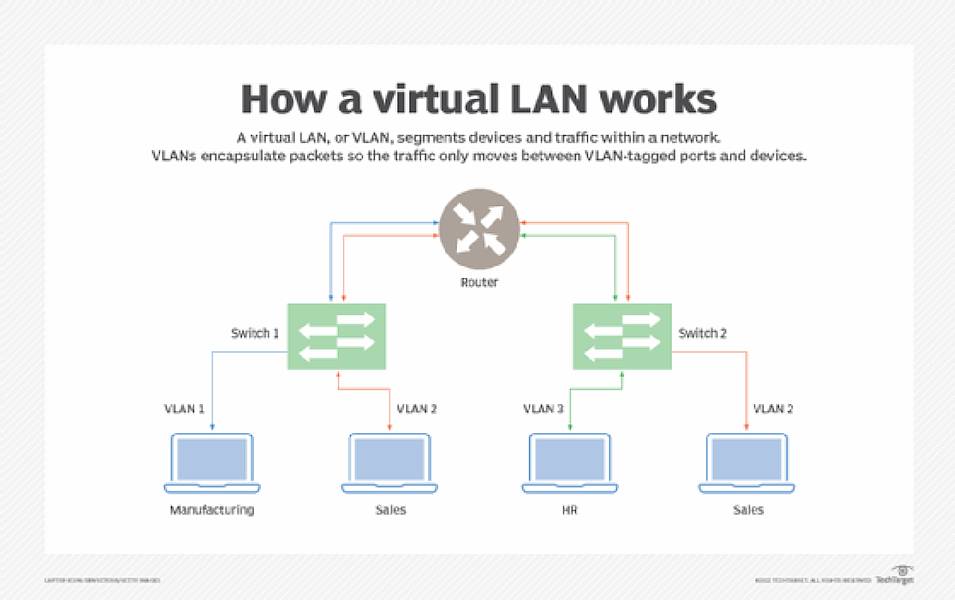
VLANs can be used for a variety of purposes. Below are some of its uses:
- Network Segmentation: VLANs allow you to segment a single physical network into multiple logical networks. This is particularly useful in large networks or organizations where different departments, teams, or groups need isolation from one another. Each VLAN operates as if it were on a separate physical network.
- Broadcast Control: In traditional flat networks, broadcasts can consume a significant portion of available network bandwidth. With VLANs, broadcast domains are smaller, which reduces the amount of broadcast traffic on each segment, improving overall network performance.
- Security: VLANs enhance network security by isolating traffic between different groups or functions within an organization. This isolation prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data or resources. For example, you can keep the HR department’s data separate from the sales department’s data.
- Efficient Bandwidth Utilization: VLANs help optimize bandwidth utilization by allowing you to assign specific resources to VLANs. This enables you to prioritize and allocate bandwidth based on the needs of each VLAN, ensuring critical applications receive the necessary network resources.
- Simplified Management: VLANs make network management more efficient. Network administrators can configure, monitor, and manage VLANs easily, making it simpler to make changes or adjustments as needed without affecting other parts of the network.
- Flexibility: VLANs are flexible and adaptable. You can reconfigure VLAN assignments without physically rewiring the network. This flexibility is especially useful in environments where network changes are frequent.
- Improved Troubleshooting: VLANs isolate network problems to specific segments, making it easier to identify and resolve issues. Troubleshooting becomes more focused, reducing downtime and improving overall network reliability.
- Guest Network Isolation: In environments where guest access is required, VLANs can be used to isolate guest traffic from the internal network, adding an extra layer of security to protect sensitive resources.
- Optimized Multicast Traffic: In multimedia and streaming applications, VLANs can be used to optimize multicast traffic delivery. Multicast groups can be defined within VLANs to ensure that only members of the specific VLAN receive the multicast data.
- When planning your network architecture, it is crucial to factor in VLANs due to their numerous advantages which includes, enhanced security, improved network performance, and streamlined manageability. These benefits are instrumental in enhancing overall network operation.

